Cities of Innovation: Hanover
Key indicators
ICT Infrastructure

Average broadband speed (Mbps)

Alternative networks available
— Available broadband speed is up to 250 Mbps — The rollout of Fibre to the home (FTTH) is still running (2011) and offers rates in a range of Gbps
Local, national and international transport links

Airport passengers
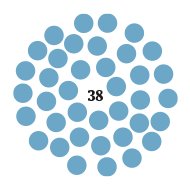
Non-stop destinations
Train station runs 750 trains a day with 250,000 passengers. Nr. 6 is the most frequented rail station in Germany Home to the largest inland harbour in northern Germany
University links and access to talent

QS World University ranking (Leibniz University Hanover)
Tertiary-educated workers
— 14 universities, 33 institutes — Key employment sectors: automotive, production, financial services; services
Costs and availability of workspace
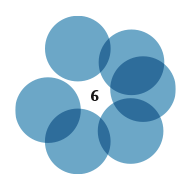
Co-working spaces

Average office rent
— 190,000 m2 new office space to be built by 2020
City support for start-ups and SMEs

Biannual competition

Events
— Biannual Startup–Impuls competition — “Boulevard of ideas” as part of an annual public festival “Maschseefest”
Financial support and access to investors & accelerators

Public funds for startups

Accelerator (Venture Villa Accelerator)
— 3 public technology centres — Bank funding, grants and discounted loans
Additional information
Local, national and international transport links
Hanover’s international airport is in the top 10 busiest in Germany, with many non-stop flights including Dubai.
Trains take 1.5 hours to Berlin and Hamburg from Hanover’s Hbf train station.
Hanover port is directly connected to the Port of Hamburg. Major motorway, or autobahn roads cross north-south (A7) and east- west (A2); it takes two hours to drive to Berlin, Hamburg or Rhineland.
City railway of 127km; subway 19km; public buses cover 510km in the region.
Hanover is a growing city of 530,000; affordable housing is available and is less expensive than in other big cities such as Berlin, Stuttgart and Munich. More than 40% of the city is green with the biggest European city forest Eilenriede, which covers 640ha.
Infrastructure is well-built with a good network of cycle lanes, ongoing building of electric vehicle charging stations, and several car- sharing options. Hanover is the first city where Volkswagen’s MOIA shuttle on-demand, electric car- sharing service is operational.
University links and access to talent
— 47,000 students
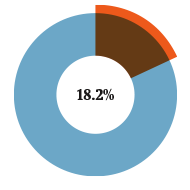
— 18.2% of the workforce are university graduates
— Collaboration between research and SMEs; postgraduates and students usually develop innovation together with SMEs and often begin their career in these companies.
Costs and availability of workspace
Several co-working spaces:
City support for start-ups and SMEs
SMEs are supported by the city of Hanover with financing, links to existing networks, advice for startups and mentoring on growing and establishing companies. The city has its own department of economic development as part of public services. Also, the state of Lower Saxony’s main funding bank is in Hanover.
Financial support and access to investors & accelerators
— €30M public funds for startups
— Several accelerators including:

