Cities of Innovation: Oxford
Key indicators
ICT Infrastructure
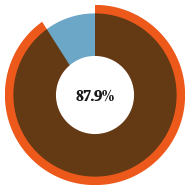
Ultrafast broadband availability

Gigabit broadband voucher
— 98.9% availability of superfast broadband (30 Mbps) — 87.9% availability of ultrafast broadband (100 Mbps) — DCMS Gigabit broadband voucher £2500
Local, national and international transport links

Heathrow airport
78 million passengers/year in 2017

Train journey to London
— 1 local airport — 65 km from London Heathrow — Motorways and train lines leading to Birmingham and Manchester and London
University links and access to talent

QS World University ranking
Oxford University

Nobel Prizes
— Oxford University: 1st in Times Higher Education ranking 2019 — 43% of the workforce with degree- level qualifications — Largest environmental data holding in the UK — 4% unemployment rate
Costs and availability of workspace

Office rent

Innovation centers
— 48 innovation centres in Oxfordshire including 11 co-working spaces in Oxford — Hot desk price in an innovation centre: €100-400 per month — Office price: between €25-70 ft2 per annuum
City support for start-ups and SMEs

Flagship events

University-led
— Venturefest Oxford–flagship events connecting entrepreneurs and innovators with investors and mentors, now UK wide — Mainly university-led programmes and grants
Financial support and access to investors & accelerators

Oxford Trust
Incubators and accelerators
— Apart from Oxford Trusts' 30 years success, the Oxford Innovation Society brings together researchers, inventors, technology transfer professionals, local companies, venture capital groups — 14 Incubators and accelerators, some managed by the University of Oxford
Additional information
Local, national and international transport links
There is one local airport – London Oxford airport
University links and access to talent
The main research facilities at Oxford University include:
Costs and availability of workspace
Co-working spaces:
— MinorOak Coworking
— Accelerate Places Nottingham
— Cobden Place
— Regus, Nottingham City Centre
City support for start-ups and SMEs
There are a lot of university-led programmes and grants. In addition, Venturefest Oxford connects entrepreneurs and innovators with investors and mentors.
Financial support and access to investors & accelerators
There are many incubators and accelerators in Oxford, including some managed by the University of Oxford, Oxford Brookes University and Harwell Campus.
Oxford Innovation Society fosters links between business and the academic community. It offers corporate membership for larger organisations, and small tech company membership.
Oxford Trust works to encourage the pursuit of science and enterprise in the region by developing Oxford’s science base and helping businesses who want to pursue scientific enterprises.
How to set up a business: a quickfire guide
What are my options?
While there are numerous business forms, the most common initial start-up structures are as a sole trader and or a private company limited by shares.
A sole trader is the simplest structure as the individual does not need to register the company with a formal constitution. Sole traders enjoy minimal paperwork and benefit from the flexibility of moulding their business plan without consulting shareholders. The downfall of this structure is that sole traders are personally liable for all the debts and contractual obligations of the business.
Private companies limited by shares give a business its own legal personality. This means that the business owners are not personally liable for the company’s debts. Companies with this structure are also able to raise capital more easily due to tax incentives and greater credibility as a result of a company’s professional image. Although this structure comes with additional paperwork, the UK’s efficient online company system has made the submission of paperwork a relatively simply task.
What do I need to set up a company?
To incorporate a company, an individual needs to submit the following:
Company name: this must not be too similar to another registered name.
Registered address: you must provide a UK office address as the address to which all business letters and invoices are sent. While there needs to be a registered address in the UK, an international director does not need to be present at the address. The director only needs to ensure that it is a physical address from where they can receive mail. Many businesses use their accountant’s address where post can then be forwarded to the director or managed by the accountant itself.
Director: the name of at least one director. Directors need to be at least 16 years old. Directors do not need to reside in or even have visited the UK. Shares: the details of share capital with at least one initial shareholder.
Company documents: a Memorandum and Articles of Association are the legal documents which confirm company formation and dictate the rules by which the company will be run. While these may seem daunting, the UK government’s website (gov.uk) has a memorandum template and model articles which a director may copy and complete easily and quickly for submission.
How much does it cost?
The entire online registration process costs £12 (€14) and it takes up to 24 hours for the company to be registered.
Tax rates
Following registration, the company will be subject to a 19% tax rate on company profits. Additionally, the company may be liable to pay VAT if its taxable turnover exceeds £85,000 annually. VAT rates vary depending on services or goods rendered with the maximum VAT rate being 20%.
The UK government strongly supports start-ups and offers various tax relief and support schemes. Tax relief is usually possible on spending that is entirely for business use such as certain business travel or machinery. R&D tax credits are available to businesses which are working to advance science or technology. A company that profits from its patented invention could also benefit from Patent Box in which corporation tax is lowered from 19% to 10%.
Small businesses can also benefit from the Seed Enterprise Investment Scheme which offers both income and capital gains tax relief to the company’s investors.
To raise further capital, the government arm Innovate UK drives growth by supporting UK- based businesses through funding. To date, the scheme has invested around £2.5 billion. Businesses may participate through regular innovation competitions, which focus on different sectors.
Legal contact
Electra Japonas and Kaveesha Thayalan
The Law Boutique
Work.Life, The Law Boutique, 5 Tanner St, Bermondsey, London SE1 3LE


